
ThermoChimie (Consortium Andra -
Ondraf/Niras -
NWS
)


ThermoChimie is a thermodynamic database initially created and developed by Andra (French National Radioactive Waste Management Agency), for more than twenty years (1995). In October 2014, Nuclear Waste Services (formerly Radioactive Waste Management Limited, UK) joined the project and the "ThermoChimie consortium" was formed. In March 2018, Ondraf/Niras (National Agency for Radioactive Waste Management, Belgium) also joined the "ThermoChimie consortium".
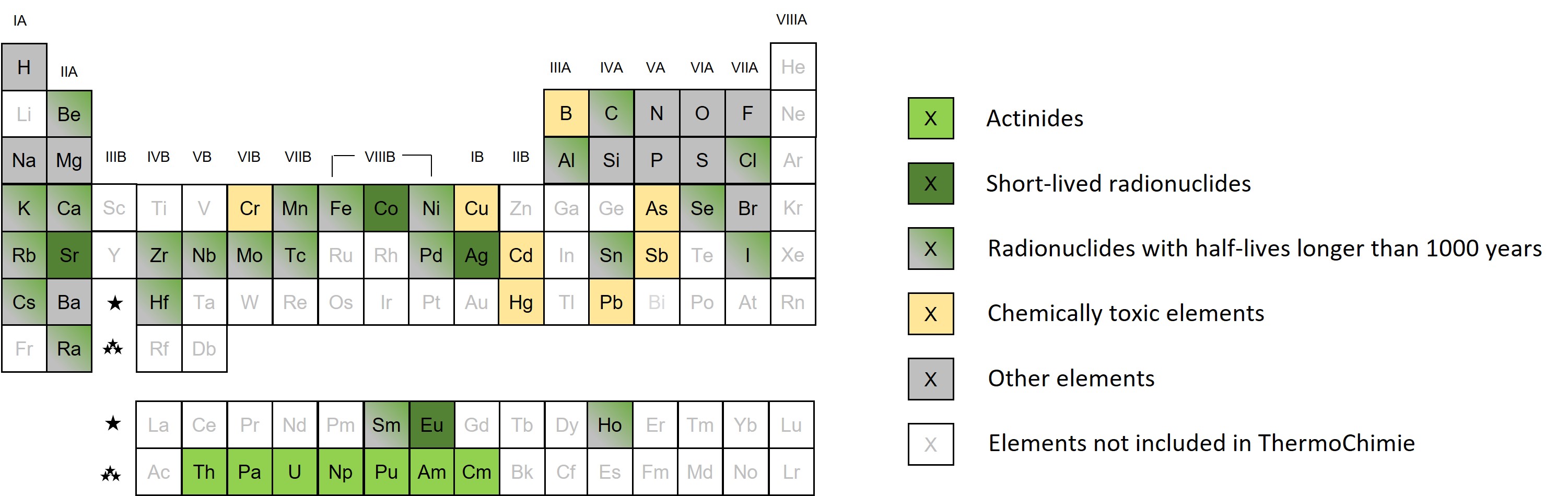
In waste management, geochemical modelling is used in support of the assessment of radionuclide and non-radiological pollutant behaviour in a range of scenarios, such as within radioactive waste packages and geological disposal facilities, through the geosphere, and in legacy contaminated land. This can be in support of repository performance assessments, research activities (such as modelling experiments), or decisions about waste conditioning, reprocessing, and disposability. However, an accurate, consistent and complete thermodynamic data set is required for these models to be meaningful.
ThermoChimie is designed to be applied over the 6 - 14 pH range at temperatures below 80°C and in systems with an Eh in the range -0.5V to +0.5V since these are the conditions generally expected within radioactive waste repositories. ThermoChimie provides robust thermodynamic data for a wide range of radionuclides and non-radiological pollutants, as well as major components expected within a geological disposal facility, including constituent host-rock mineral phases, bentonites, cements, and their evolving secondary phases. However, the database can be applied to other systems within the water stability domain. These thermodynamic data are mainly derived from comprehensive, active literature studies and are supplemented by an experimental program when required.
|
|
|